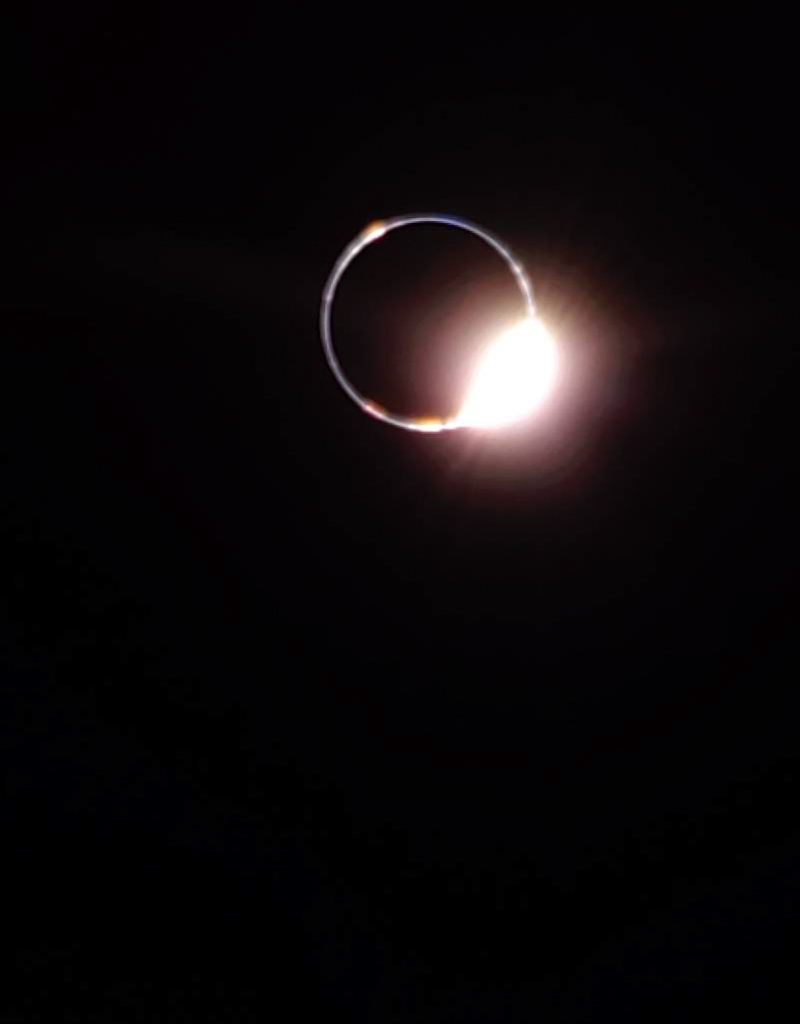
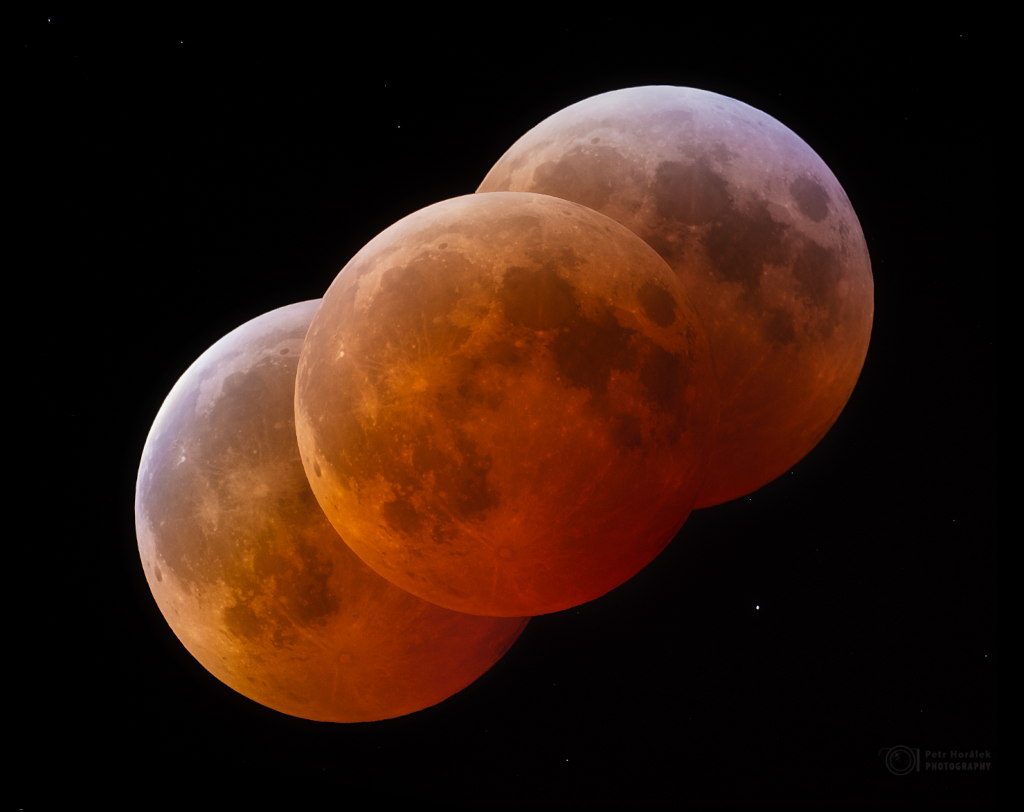
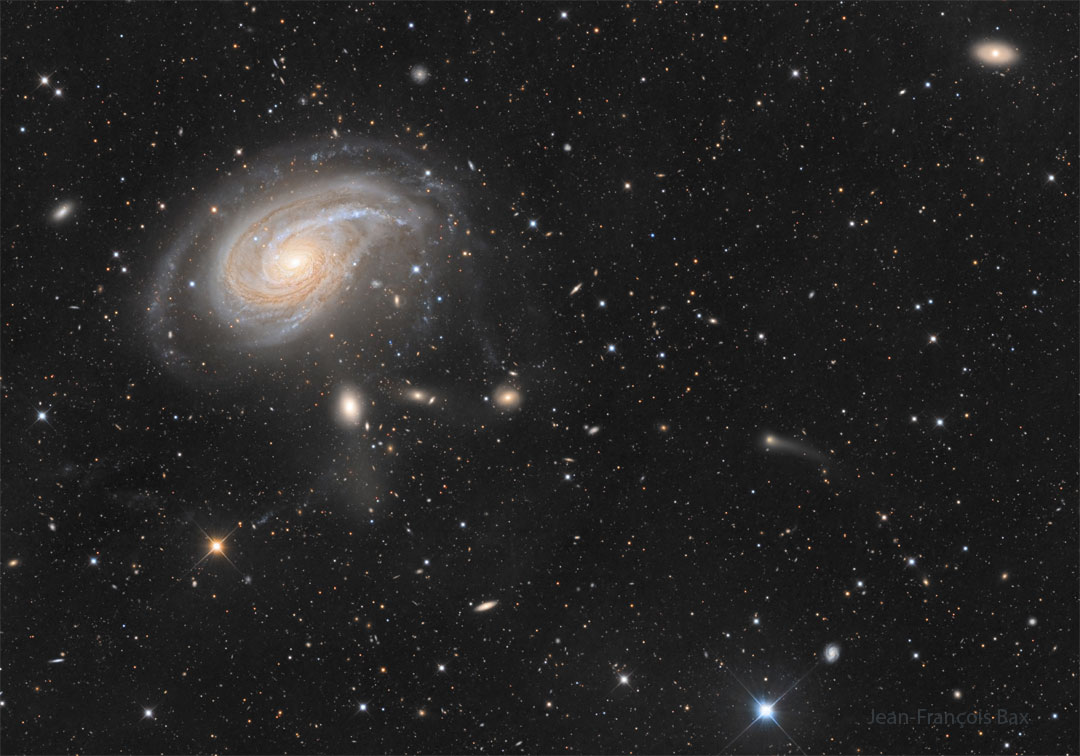
Recorded from 2024 March 10, to 2025 March 1, this composited series of images reveals a pattern in the seasonal drift of the Sun’s daily motion through planet Earth’s sky. Known to some as an analemma, the figure-eight curve was captured in exposures taken on the indicated dates only at 18:38 UTC from the exact same location south of Stephenville, Texas. The Sun’s position on the 2024 solstice dates of June 20 and December 21 would be at the top and bottom of the curve and correspond to the astronomical beginning of summer and winter in the north. Points that lie along the curve half-way between the solstices would mark the equinoxes. The 2024 equinox on September 22, and in 2025 the equinox on March 20 (today) are the start of northern fall and spring. And since one of the exposures was made on 2024 April 8 from the Stephenville location at 18:38:40 UTC, this analemma project also reveals the solar corona in planet Earth’s sky during a total solar eclipse. [via NASA] https://ift.tt/WXNQd7S